Top AI Tools for BIM Architects in 2026
Jan 7, 2026
The role of the BIM architect has shifted. In 2026, the question is no longer if you should use AI, but how to integrate it without disrupting the precision required by Building Information Modeling. The most effective tools today do not attempt to replace the architect; instead, they automate the friction points -visualization, documentation, site analysis, and feasibility- allowing the BIM model to remain the single source of truth.
This guide evaluates five established AI tools that fit naturally into professional BIM workflows, moving beyond experimental tech to reliable, daily drivers.
Evaluation Criteria
To select these tools, we focused on practical utility for architectural professionals rather than novelty.
BIM Interoperability: Does the tool respect the geometry and data in Revit, Archicad, or Rhino?
Workflow Friction: Can a user get a result in minutes, or does it require extensive training?
Output Reliability: Are the results consistent enough to show a client or consultant?
Professional Utility: Does it solve a real problem (e.g., rendering, parking counts, energy codes)?

Comparison Table
Feature | Rendair AI | Autodesk Forma | TestFit | Cove.tool | Glyph |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Primary Function | Visualization & Rendering | Site Planning & Analysis | Generative Feasibility | Energy & Carbon Analysis | Documentation Automation |
Best For | Rapid client presentations | Early-stage massing | Multifamily & Industrial | Sustainability compliance | Revit production tasks |
Learning Curve | Low (Intuitive) | Medium | Medium | Medium | Low |
Integration | Image-based (Universal) | Cloud/Revit | Revit/Dynamo | Web/Plugin | Revit Plugin |
Detailed Reviews
1. Rendair AI
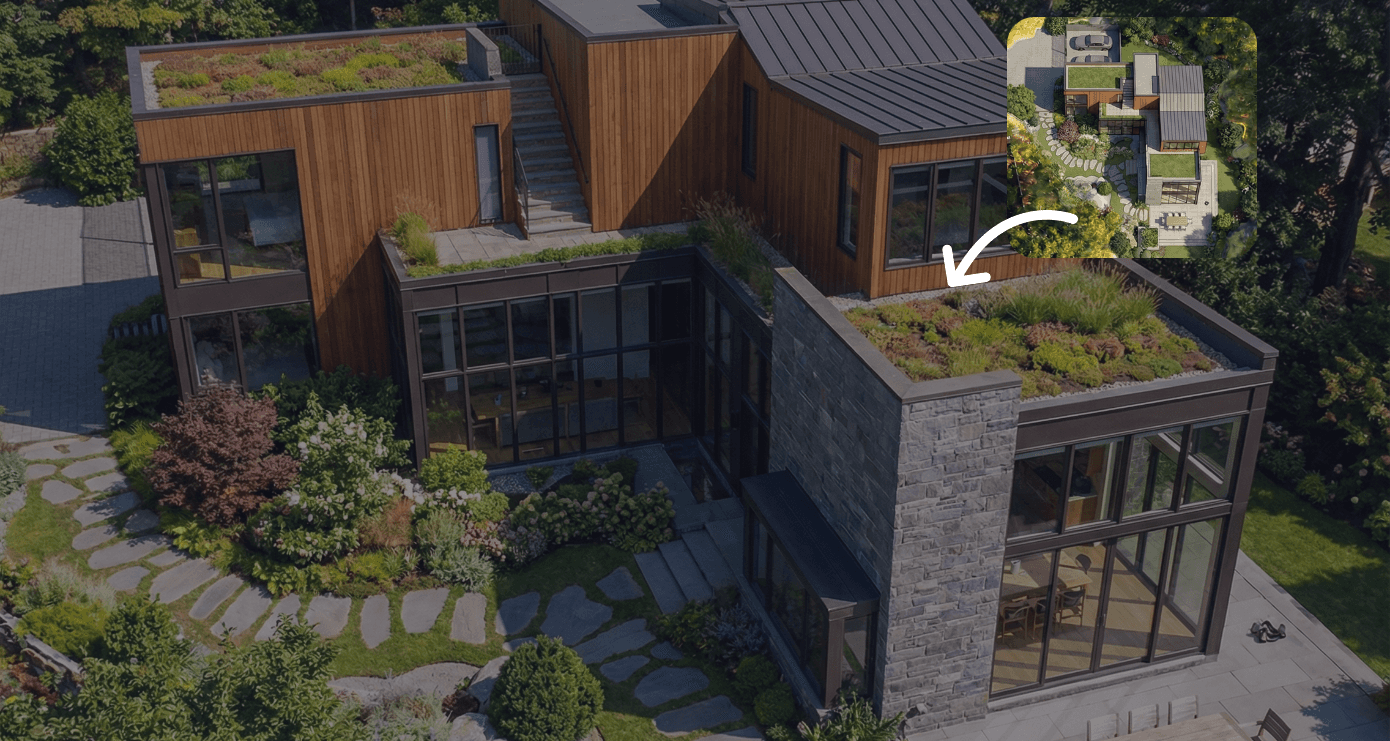
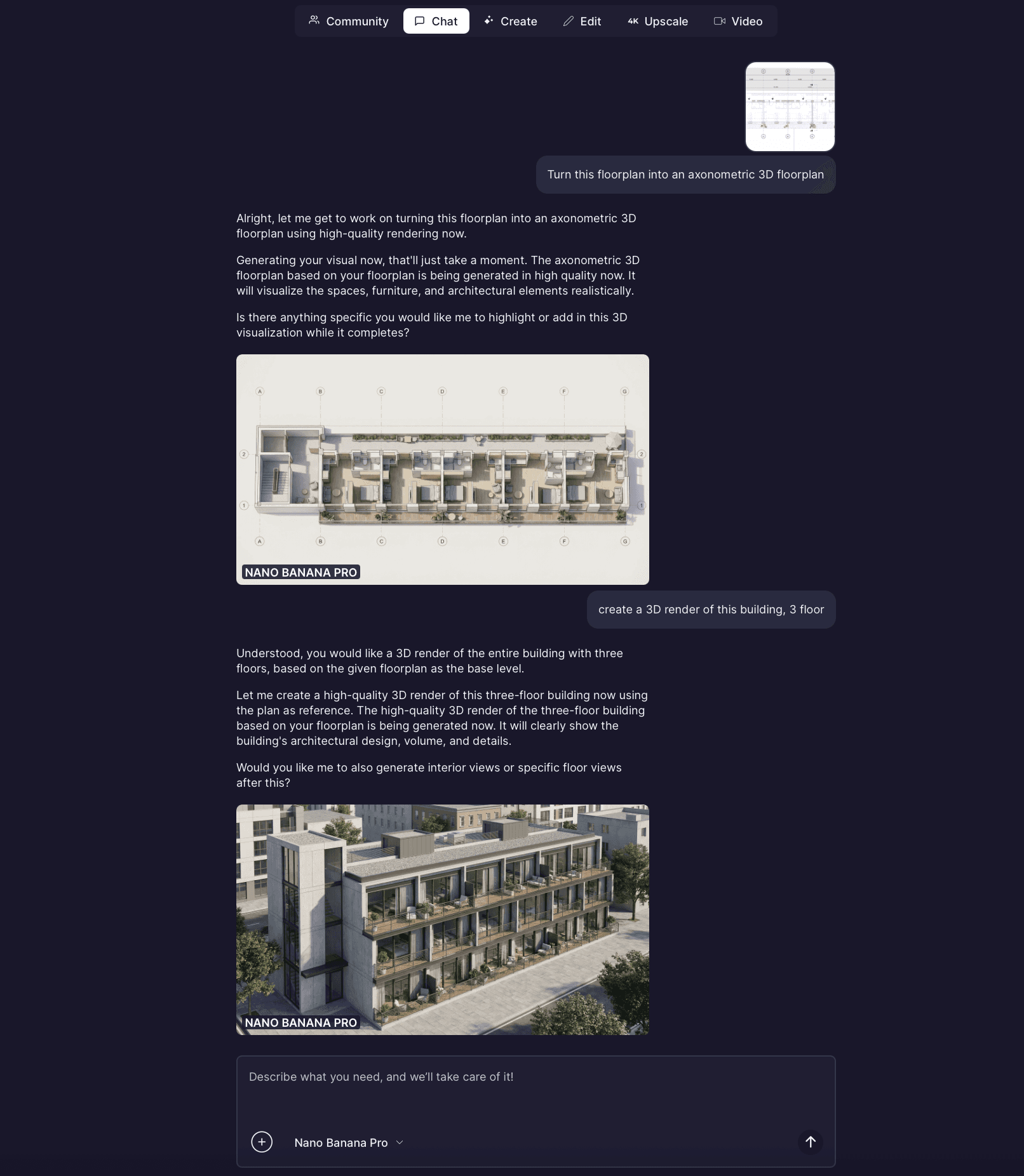
Rendair AI has established itself as a premier visualization partner for BIM architects who need high-fidelity results without leaving their design mindset. Unlike complex rendering engines that require managing lighting rigs and textures, Rendair interprets architectural intent directly from screenshots, sketches, or clay models. It bridges the gap between a raw BIM viewport and a client-ready presentation.
Key Features:
Sketch-to-Render: Instantly converts rough BIM screenshots or hand sketches into photorealistic images.
Material Consistency: accurately interprets architectural materials (concrete, glass, timber) without manual mapping.
Inpainting & Editing: Allows users to modify specific parts of a render (e.g., "change flooring to oak") without re-rendering the whole scene.
Upscaling: Generates high-resolution outputs suitable for large-format printing or marketing boards.
Best For: Architects who need to visualize design options rapidly during the concept and design development phases.
Highlight: The "Creativity Strength" slider allows precise control over how strictly the AI adheres to the original BIM geometry, ensuring the generated image matches the actual design.
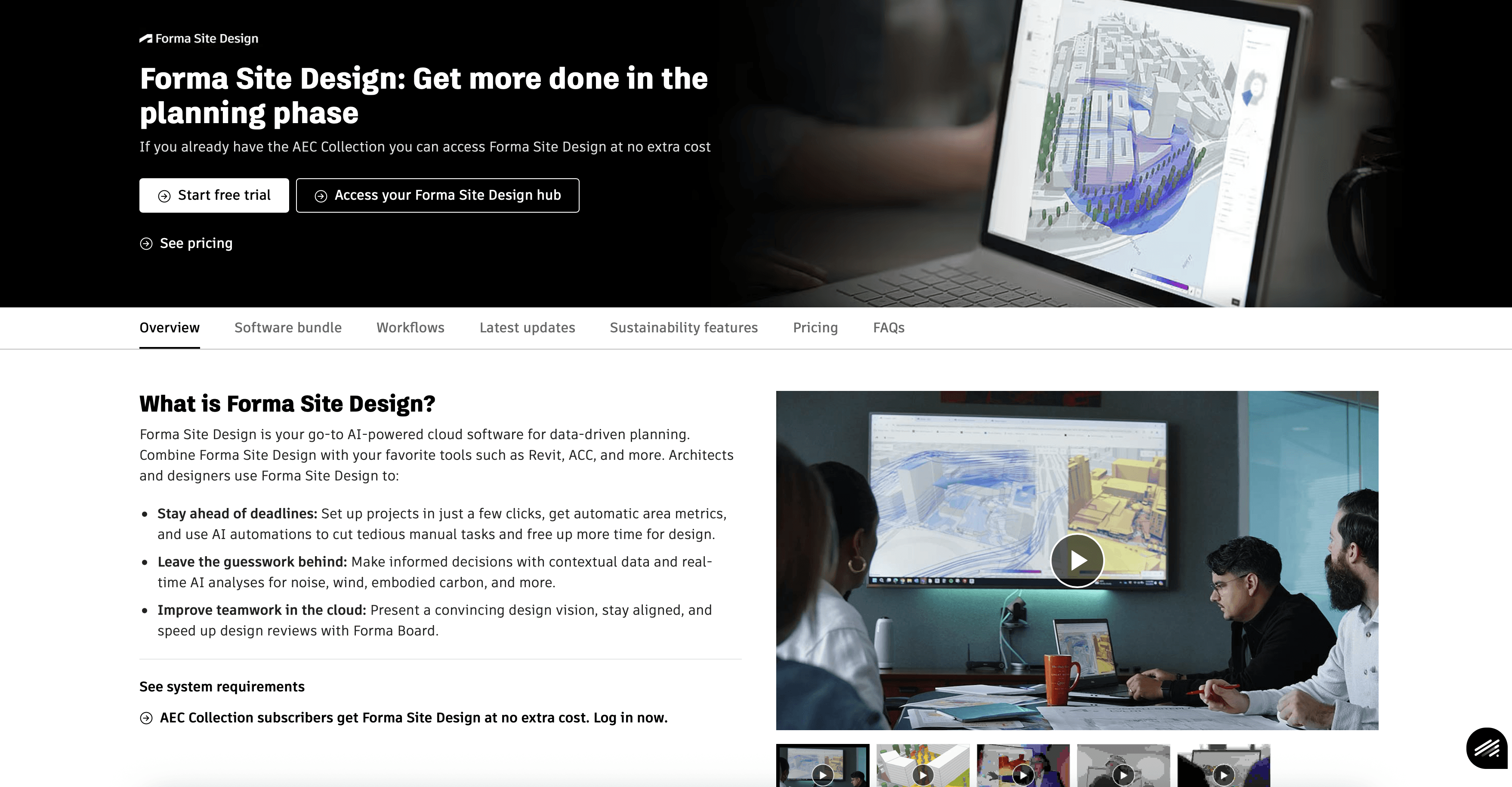
2. Autodesk Forma
Formerly known as Spacemaker, Autodesk Forma is a cloud-based AI tool that focuses on the pre-design and planning phase. It helps architects analyze site constraints before they ever draw a wall in Revit. By automating environmental analyses—such as wind, noise, and daylight—Forma allows BIM architects to make data-driven decisions early, reducing the risk of costly revisions later.
Key Features:
Real-time Analysis: Instantly calculates sun hours, daylight potential, and wind comfort on massing models.
Generative Layouts: Proposes site layouts based on density targets and constraints.
Revit Synchronization: Sends the selected massing proposal directly into Revit as native geometry.
Best For: Urban planners and architects conducting feasibility studies and site analysis.
Consideration: It is primarily an early-stage tool; detailed design still happens in Revit.
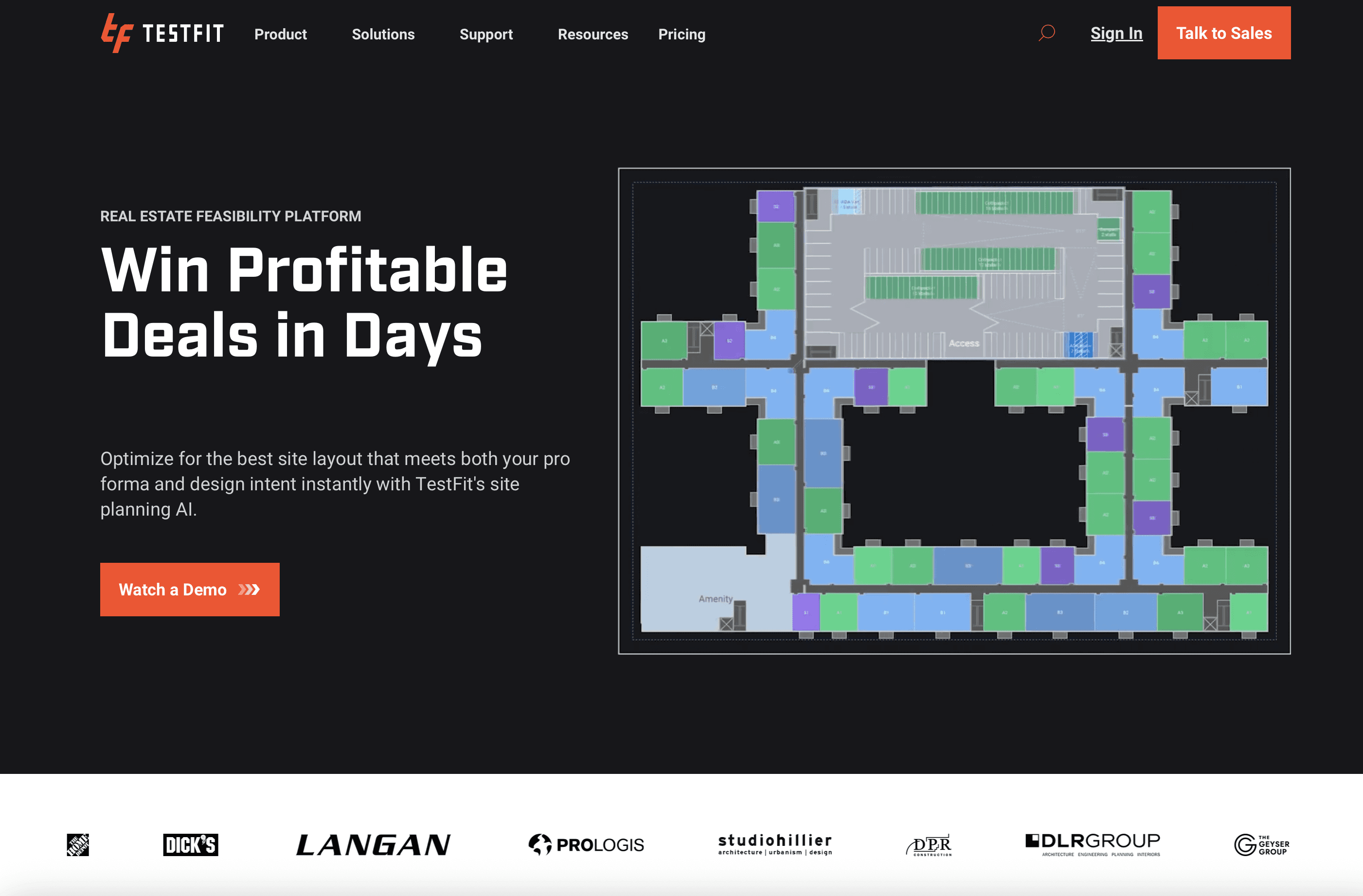
3. TestFit
TestFit solves the mathematical and geometric complexities of site feasibility, particularly for commodity buildings like multifamily housing, hotels, and industrial warehouses. It uses generative design algorithms to solve site layouts in milliseconds. For a BIM architect, this means instant answers to "how many units fit on this site?" and "does the parking count work?"
Key Features:
Real-time Deal Solving: Adjusts unit mix and building shape instantly while updating parking ratios and yield on cost.
Generative Design: Solves for thousands of iterations based on strict parameters (setbacks, height limits).
BIM Connection: Exports optimized geometry to Revit, SketchUp, or DXF for further development.
Best For: Architects working with developers who need rapid feasibility answers and yield maximization.
Consideration: The geometry is strictly logic-driven, making it less suitable for highly bespoke or sculptural architectural forms.
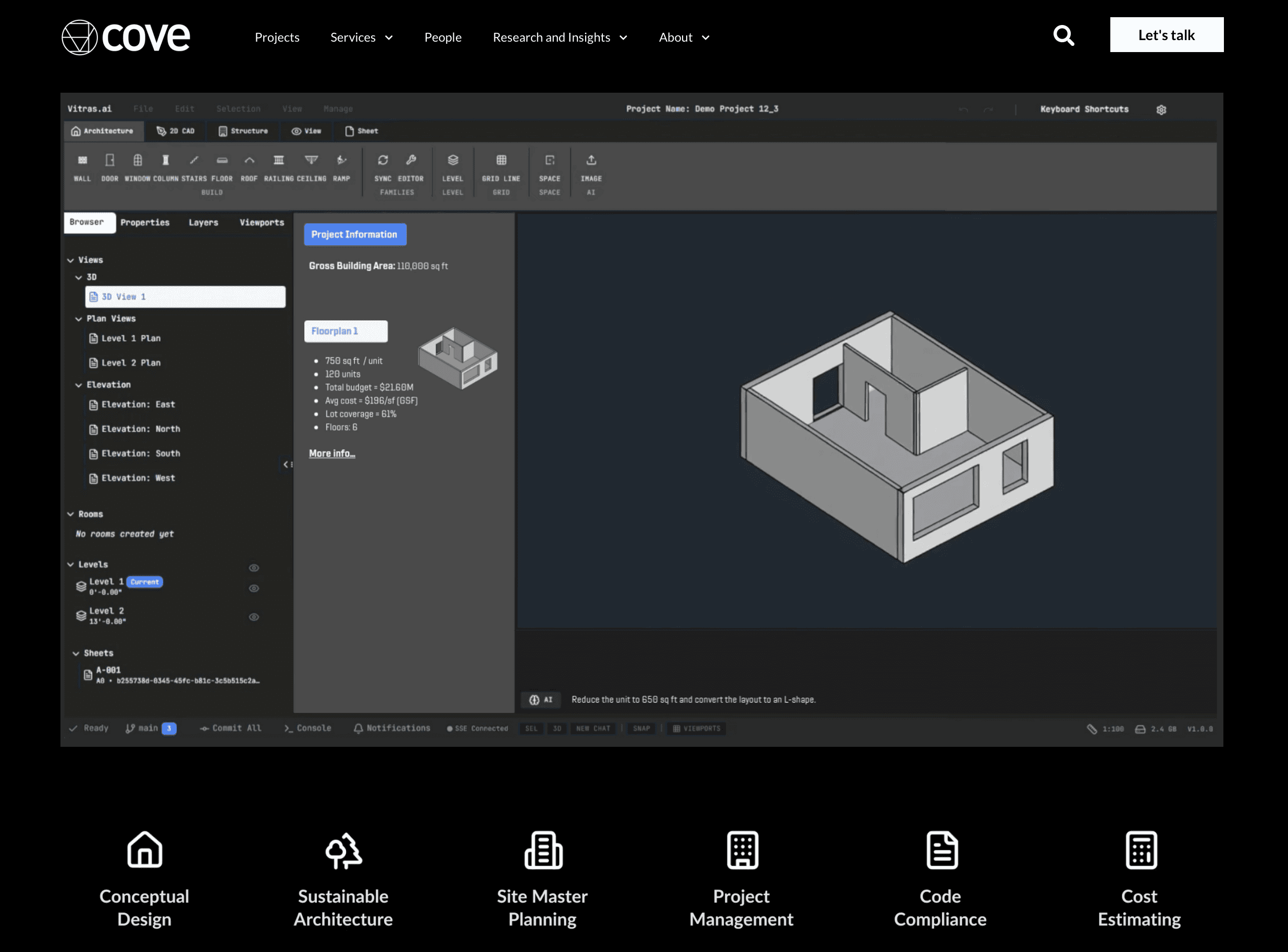
4. Cove.tool
Cove.tool is an automated building performance platform that integrates analysis into the BIM workflow. It democratizes energy modeling, allowing architects to understand the carbon and cost implications of their design decisions without waiting for a specialized engineer. It is essential for meeting 2030 targets and strict energy codes.
Key Features:
Automated Energy Modeling: rapid analysis of EUI (Energy Use Intensity) and carbon footprint.
Cost vs. Energy Optimization: Helps teams find the most cost-effective way to meet energy goals (e.g., better glass vs. more insulation).
Daylight & Glare Analysis: Visualizes sDA (Spatial Daylight Autonomy) and ASE (Annual Sunlight Exposure).
Best For: Firms prioritizing sustainability and needing to prove code compliance or LEED certification early.
Consideration: Requires a clean, simplified geometry export from the BIM model for accurate results.
5. Glyph (by EvolveLAB)
While the other tools on this list focus on design and analysis, Glyph focuses on the tedious production work in Revit. It is a plugin that automates documentation tasks, such as tagging, dimensioning, and sheet creation. By handling the repetitive "click-heavy" work, it frees up the BIM architect to focus on design and coordination.
Key Features:
Automated Tagging: Automatically places tags on rooms, doors, windows, and equipment in views.
Smart Dimensioning: Generates dimensions for walls and grids based on user-defined rules.
Sheet Packing: Automates the placement of views onto sheets to maximize space.
Best For: Production teams and BIM managers looking to reduce the hours spent on construction documentation.
Consideration: It is specific to the Revit ecosystem and requires setup to match firm standards.
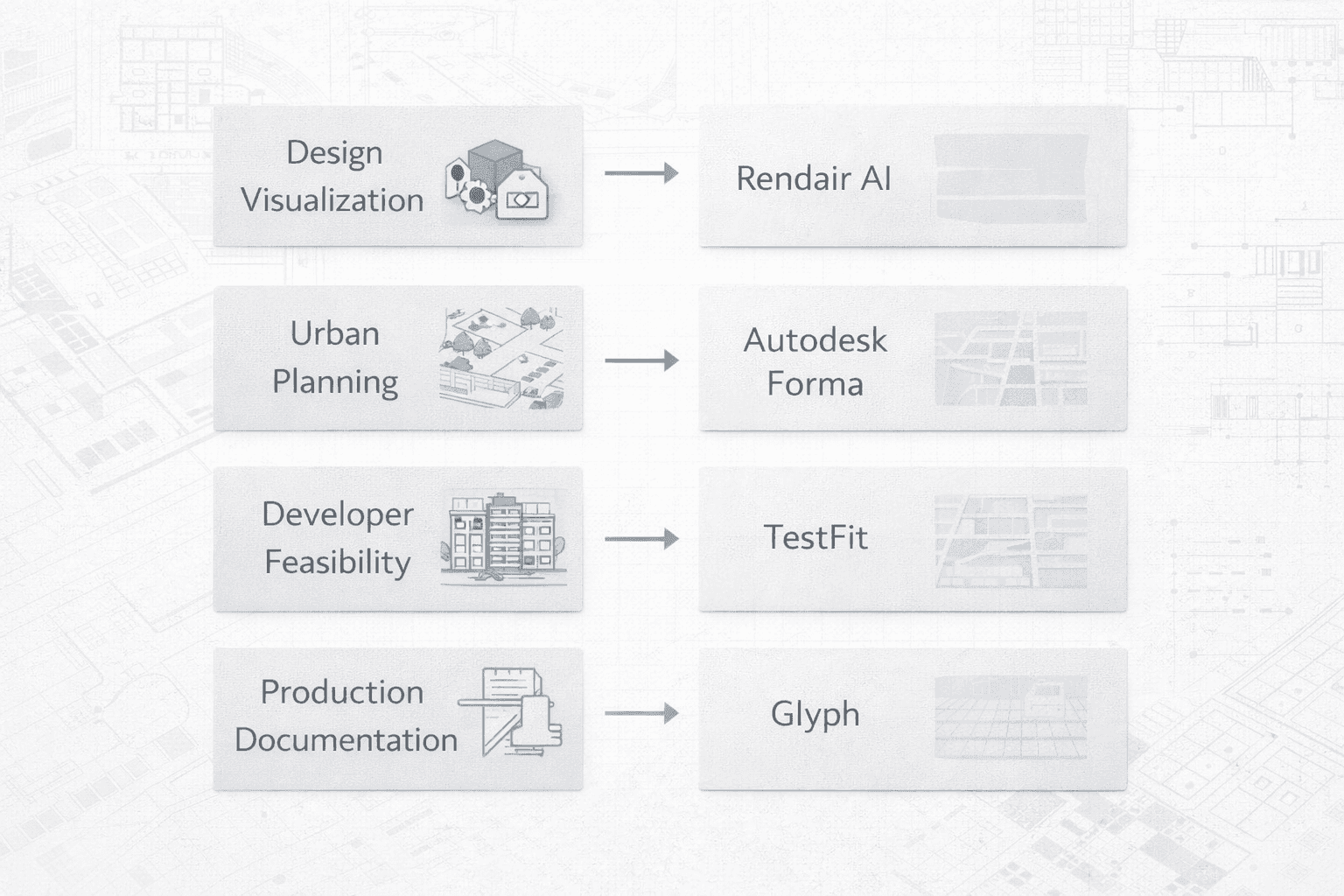
Common BIM + AI Workflows
The Feasibility Sprint
Workflow: Use TestFit to generate a maximised site layout and parking configuration. Export the massing to Autodesk Forma to check for wind tunnels and daylight quality.
Tools: TestFit, Autodesk Forma
The Client Presentation
Workflow: Take a viewport screenshot from your Revit or Archicad model. Upload it to Rendair AI to generate three different material options (e.g., brick vs. timber facade) in minutes for a client meeting.
Tools: Revit/Archicad, Rendair AI
The Sustainable Permit Set
Workflow: Export the building envelope to Cove.tool to optimize glazing ratios for energy compliance. Once the design is fixed, use Glyph to automatically tag and dimension the floor plans in Revit.
Tools: Cove.tool, Glyph, Revit
Choosing the Right Tool
For Design Visualization: If your bottleneck is producing high-quality images from BIM models, start with Rendair AI. It offers the highest visual return on time invested.
For Urban Planning: If you deal with complex sites and environmental constraints, Autodesk Forma provides the necessary analytical data.
For Developer Work: If your clients demand rapid unit counts and yield analysis, TestFit is the industry standard for feasibility.
For Production: If your team is drowning in drafting tasks, Glyph offers immediate ROI by automating documentation.
FAQ
Will these tools replace BIM software like Revit or Archicad?
No. These tools are "copilots" or specialized engines that feed into or read from your BIM software. The BIM model remains the central database for the project.
Are the generated images from Rendair AI copyright safe?
Yes. Rendair AI provides commercial usage rights for the images you generate, making them safe for client presentations and marketing materials.
Do I need a high-end computer to run these?
Most of these tools (Rendair, Forma, Cove.tool) are cloud-based, meaning the heavy processing happens on their servers, not your laptop. Plugins like Glyph and TestFit rely on local hardware but are generally lightweight compared to the BIM software itself.
Is AI in 2026 accurate enough for construction documents?
AI for generative geometry (like TestFit) is accurate, but AI for documentation (like Glyph) still requires human review. The goal is to get 90% of the work done automatically, leaving the architect to verify the final 10%.
Conclusion
The landscape of architectural tools in 2026 favors the connected workflow. The most successful firms are those that stop viewing AI as a novelty and start treating it as a standard utility—using it to render, calculate, and document faster than before.
By integrating tools like Rendair AI for visualization and specialized engines for analysis and documentation, BIM architects can return to what they do best: designing spaces that work for people.
To experience how AI can streamline your visualization process today, try creating your first render with Rendair.
Recent Posts
Tools
Step-by-step Design a House on a Real Site Photo
Discover the top 5 AI tools for BIM architects in 2026 that streamline visualization, feasibility, and documentation.
Tools
Enscape vs Twinmotion: Which Real-Time Render Engine Wins in 2026?
Discover the top 5 AI tools for BIM architects in 2026 that streamline visualization, feasibility, and documentation.
Tools
Octane Render vs Redshift: Which GPU Renderer is Best?
Discover the top 5 AI tools for BIM architects in 2026 that streamline visualization, feasibility, and documentation.
Tools
D5 Render vs Enscape: Which Real-Time Engine Fits Your Workflow?
Discover the top 5 AI tools for BIM architects in 2026 that streamline visualization, feasibility, and documentation.
Tools
Lumion vs Unreal Engine: Architectural Rendering Comparison
Discover the top 5 AI tools for BIM architects in 2026 that streamline visualization, feasibility, and documentation.
Tools
Blender vs D5 Render: A Comprehensive Comparison for Architects
Discover the top 5 AI tools for BIM architects in 2026 that streamline visualization, feasibility, and documentation.
Join 500,000+ architects who saved time. No credit card needed for your first 20 credits.







